Why Do We Need Wastewater Treatment
Understanding the Essential Role of Wastewater Treatment
In an increasingly urbanized and industrialized world, the importance of wastewater treatment cannot be overstated. Modern society generates vast amounts of wastewater that, if left untreated, could pose severe threats to public health, the environment, and economic stability. Despite being a hidden layer of our infrastructure, wastewater treatment plays an essential role in ensuring sustainable living. This article delves into the depths of why we need wastewater treatment, exploring its environmental, health, and economic impacts.
What is Wastewater?
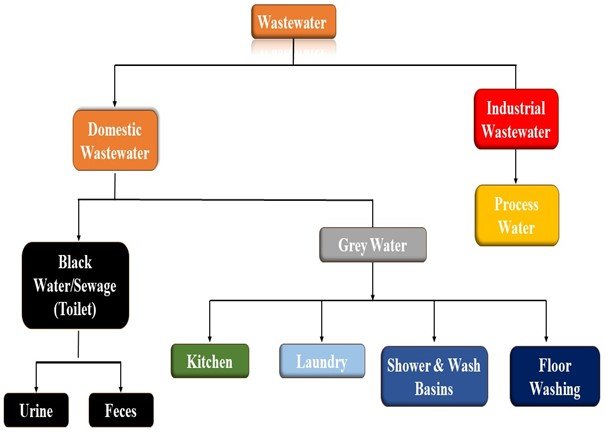
Before diving into the specifics of why wastewater treatment is necessary, it’s important to understand what wastewater is. Wastewater is any water that has been affected by human use. It originates from a variety of sources, including domestic households, industrial processes, agricultural activities, and stormwater runoff. In homes, wastewater comes from kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms, encompassing everything from washing dishes to flushing the toilet. Industrial wastewater, on the other hand, includes water discharged from processes like manufacturing, mining, and chemical processing.
The Environmental Impacts of Untreated Wastewater
One of the most compelling arguments for the necessity of wastewater treatment is its environmental impact. Untreated wastewater can degrade ecosystems, harm wildlife, and alter natural water bodies.
Water Pollution
When untreated wastewater is discharged into rivers, lakes, or oceans, it leads to water pollution. This pollution alters the quality of the water, making it unsafe for wildlife and human consumption. Specifically, pollutants like nitrogen, phosphorus, heavy metals, and pathogens present in wastewater can lead to severe ecological consequences. Nutrient-rich wastewater can cause eutrophication, where excessive nutrients stimulate the growth of algae. This can deplete oxygen in water, killing fish and other aquatic organisms.
Harm to Aquatic Life
Heavy metals and toxic chemicals, if not adequately removed from wastewater, can contaminate water bodies and bioaccumulate in the food chain, posing risks to aquatic life and, ultimately, humans who consume seafood. Similarly, pathogenic organisms present in untreated wastewater can lead to diseases in aquatic species.
Groundwater Contamination
When untreated or insufficiently treated wastewater percolates into the ground, it can contaminate groundwater resources. Groundwater is a critical source of drinking water for many people worldwide, and contamination can make it unsafe for human use and difficult to remediate.
The Health Imperatives
Human health is intricately connected to water quality. Untreated wastewater harbors numerous pathogens and chemicals that pose direct threats to human health.
Spread of Diseases
Wastewater contains pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and hepatitis. When humans come into contact with contaminated water — whether through drinking, agriculture, or recreation — these diseases can quickly spread. Treatment processes are crucial in removing these pathogens, safeguarding public health.
Antibiotic Resistance
There’s growing concern about the role of wastewater in the spread of antibiotic resistance. Wastewater can carry antibiotic-resistant bacteria and residual pharmaceuticals, which, when released into the environment, can facilitate the spread of resistance. Treating wastewater helps to mitigate this issue by removing antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant genes.
Chemical Exposure
Industries discharge various chemicals into sewage systems. Untreated, these chemicals can end up in drinking water supplies, leading to chronic health effects such as cancer, hormonal disruptions, and developmental disorders. Effective wastewater treatment ensures these chemicals are removed or reduced to safe levels.
Economic Considerations
Beyond environmental and health concerns, wastewater treatment is also essential for economic reasons.
Protecting Fisheries and Tourism
Polluted water bodies can have devastating impacts on activities such as fishing and tourism. Fisheries depend on clean water to sustain healthy fish populations. Contaminated water can kill fish and make them unsafe for consumption, affecting livelihoods and food security. Likewise, polluted beaches and rivers deter tourists, impacting local economies.
Infrastructure and Property Values
Water pollution can lead to the deterioration of infrastructure, as contaminated water can corrode pipes and buildings. Furthermore, properties located near polluted water bodies often see a decrease in value. Effective wastewater treatment protects infrastructure and helps maintain property values.
Resource Recovery
Modern wastewater treatment plants are not just about treating water but also recovering valuable resources. Byproducts such as biogas from anaerobic digesters can be used as a renewable energy source. Similarly, nutrients like phosphorus can be extracted and used as fertilizers, creating economic opportunities and promoting sustainable practices.
Regulatory and Legal Aspects
Governments worldwide recognize the importance of wastewater treatment, enacting laws and regulations to manage it.
Legal Compliance
In many countries, stringent regulations exist regarding wastewater discharge. Industries and municipalities are legally required to treat wastewater to certain standards before releasing it into the environment. Non-compliance can result in heavy fines and legal actions, underscoring the need for proper wastewater treatment systems.
International Guidelines
On a global scale, organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations (UN) set guidelines and promote initiatives to improve wastewater treatment and management, highlighting its critical importance in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Technological Advances in Wastewater Treatment
The necessity of wastewater treatment has spurred technological advancements in the field. These innovations not only enhance treatment efficiency but also reduce costs and environmental footprint.
Advanced Filtration and Membrane Technologies
Technologies such as membrane bioreactors (MBRs) and reverse osmosis (RO) offer high levels of water purification, capable of removing dissolved solids and pathogens with high efficiency. These technologies are particularly useful in areas with limited water resources, enabling the reuse of treated water for various purposes.
Biological Treatment
Biological treatment processes harness the natural capabilities of microorganisms to degrade organic matter in wastewater. Systems such as activated sludge and trickling filters are common in municipal treatment plants, providing effective and sustainable solutions.
Decentralized Treatment Systems
Decentralized wastewater treatment systems offer a flexible solution, especially in areas where centralized systems are not feasible due to geographical or economic constraints. These systems treat wastewater at or near the source, which reduces infrastructure costs and can provide water reuse options in localized settings.
Addressing Climate Change and Adaptation
With climate change posing new challenges in water management, wastewater treatment is increasingly seen as a method of adaptation.
Managing Increased Rainfall and Flooding Events
Climate change can lead to more intense and frequent rainfall, overwhelming existing sewage systems and causing untreated wastewater to overflow into natural water bodies. Upgraded wastewater treatment facilities can manage these increased loads, reducing the risk of pollution during storm events.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Modern wastewater treatment facilities incorporate technology to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation. For example, optimizing aeration processes and recovering methane for energy use can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of treatment plants.
Public Awareness and Community Involvement
The success of wastewater treatment projects often depends on public engagement and community involvement.
Educating the Public
Raising awareness about the importance of wastewater treatment and encouraging responsible water use can lead to more sustainable water management. Public education campaigns can help communities understand how their actions contribute to wastewater issues and solutions.
Encouraging Collaboration
Stakeholder collaboration is crucial for achieving better wastewater management. This includes partnerships between governments, industries, and communities to develop and implement effective treatment and reuse systems.
Conclusion
The need for wastewater treatment is evident across multiple dimensions — environmental, health, economic, regulatory, and technological. It serves as a backbone for modern civilization, protecting ecosystems, public health, and promoting sustainable development. Investing in wastewater treatment infrastructure is not just a necessity but an opportunity to create resilient, clean water systems that benefit both people and the planet.
As we continue to face global challenges like population growth, urbanization, and climate change, the importance of advanced and efficient wastewater treatment systems will only grow. By understanding and addressing these needs, we can work towards a future where water sustainability is secured for generations to come.