Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant and Sewers
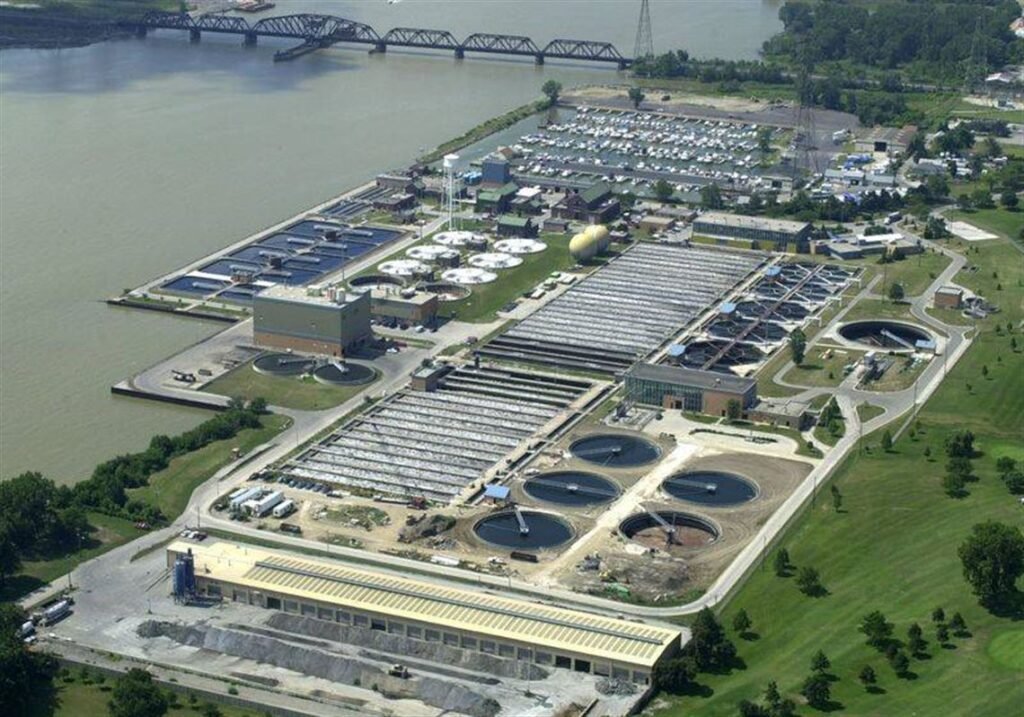

Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant and Sewers: An Essential Infrastructure for a Growing City
Introduction
Toledo, Ohio, a city known for its robust history and vibrant community, stands upon a foundation of critical infrastructure that ensures the wellbeing and sustainability of its population. Among the essential components of this infrastructure is the Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant and its extensive sewer network. This article will dissect the multifaceted aspects of this facility, including its service scope, operational capacity, recent improvements, key projects, and community interactions.
Serving a Growing Population
The Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant serves a significant portion of Toledo’s approximately 270,000 residents, along with several neighboring communities. This plant plays a pivotal role in managing and treating the wastewater generated by residences, businesses, and industries across the metropolitan area. Given the region’s mixed urban and suburban development, the plant handles a combination of domestic sewage, industrial effluents, and stormwater runoff.
Volume and Treatment Capacity
On an average day, the Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant treats around 75 million gallons of wastewater. However, during peak periods, such as heavy rainfall or snowmelt events, the volume can surge to over 150 million gallons per day. In recent years, capacity upgrades have enabled the plant to handle these fluctuations more efficiently. These upgrades encompass both hydraulic capacity enhancements to manage flow surges and advanced treatment technologies to meet stringent environmental standards.
Treatment Processes and Technologies
The wastewater treatment process at Toledo Bay View Park is multi-faceted, involving several stages to ensure the safe discharge of treated effluent into the Maumee River, which ultimately feeds into Lake Erie. The treatment process includes the following key stages:
-
- Preliminary Treatment: Screening and grit removal to eliminate large solids and debris.
-
- Primary Treatment: Sedimentation tanks allow solid particles to settle.
-
- Secondary Treatment: Biological treatment using activated sludge processes to degrade dissolved and suspended biological matter.
-
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced filtration and disinfection techniques, often involving chlorination and dechlorination or ultraviolet radiation to eliminate pathogens.
-
- Sludge Treatment: Anaerobic digestion of biosolids produces methane gas, which can be harnessed for energy, and reduces the volume of waste requiring disposal.
Recent Local News and Community Engagement
In recent news, the Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant has garnered attention due to its significant upgrades and initiatives aimed at improving the region’s wastewater management. Notably, in 2022, the plant completed a $200 million expansion project to increase its treatment capacity and incorporate state-of-the-art technology.
Community engagement has been a cornerstone of these initiatives. The Toledo Waterways Initiative, a collaborative effort involving city officials, environmental organizations, and residents, has been instrumental in driving public awareness and support for the upgrades. Numerous public meetings, informational sessions, and school outreach programs have emphasized the importance of maintaining and investing in the wastewater treatment infrastructure.
Key Projects: Strengthening the Backbone
Several key projects at the Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant underscore the city’s commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable infrastructure.
Enhanced Nutrient Removal Project
One of the hallmark projects is the Enhanced Nutrient Removal (ENR) initiative, aimed at reducing nitrogen and phosphorus levels in the treated effluent. Excessive nutrients can lead to harmful algal blooms in the Maumee River and Lake Erie, adversely affecting water quality, aquatic life, and public health. The ENR project involves installing advanced biological nutrient removal systems and optimizing existing processes to achieve stringent nutrient discharge limits.
Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Abatement
Like many older cities, Toledo’s sewer system includes combined sewers that collect both stormwater and sewage. During heavy rainfall, the system can become overwhelmed, leading to Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs) that discharge untreated wastewater into water bodies. To address this issue, the Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant has undertaken a comprehensive CSO Abatement Program. This involves constructing underground storage tanks, enhancing sewer capacity, and implementing green infrastructure solutions like rain gardens and permeable pavements to manage stormwater at its source.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Integration
In alignment with global trends towards sustainable energy practices, the plant has implemented several projects to improve energy efficiency and integrate renewable energy sources. Upgrades to the facility’s aeration systems, which are the most energy-intensive component of wastewater treatment, have significantly reduced energy consumption. Additionally, the plant’s anaerobic digesters produce biogas, a renewable energy source, which is utilized to generate electricity and heat for the facility, further reducing its carbon footprint.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite these advances, the Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant faces ongoing challenges. Aging infrastructure, climate change impacts, and regulatory changes require continuous investment and innovation. Maintaining financial stability while funding large-scale capital projects presents a balancing act for the city’s administration.
Looking ahead, the future outlook for the plant is promising. Continued emphasis on sustainability, resilience, and technological innovation will be essential in meeting the needs of Toledo’s growing population and protecting the valuable water resources of the Maumee River and Lake Erie.
Community Engagement and Education
Effective wastewater management is not solely reliant on technical expertise but also on active community engagement. The Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant has prioritized public education and transparency, recognizing that an informed community is a powerful ally.
Public Tours and Open Houses
The plant regularly hosts public tours and open houses, providing residents with a first-hand look at the treatment processes and ongoing projects. These events demystify the often-overlooked world of wastewater management, fostering a sense of civic pride and responsibility. Attendees gain insight into the complexity and importance of wastewater treatment, understanding how their daily activities impact the local water ecosystem.
School Programs and Partnerships
Educational outreach is another critical component. The plant collaborates with local schools and universities to offer educational programs, workshops, and internships. These initiatives inspire the next generation of environmental stewards and highlight career opportunities in the field of water and wastewater management. Partnering with educational institutions also facilitates valuable research collaborations, driving innovation and best practices within the facility.
Transparent Communication
Transparency in communication is vital for maintaining public trust and support. The Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant maintains an active presence on social media, providing real-time updates on projects, community events, and environmental initiatives. Regular newsletters and reports keep residents informed about water quality issues, conservation tips, and the plant’s performance metrics. This open dialogue ensures that the community remains engaged and supportive of the plant’s endeavors.
Conclusion
The Toledo Bay View Park Wastewater Treatment Plant and its extensive sewer network are cornerstones of the city’s infrastructure, safeguarding public health and the environment. Through continuous upgrades, innovative projects, and robust community engagement, the plant exemplifies excellence in wastewater management. As Toledo continues to grow and evolve, the plant will remain an essential asset, ensuring a sustainable and resilient future for the region. The collaborative efforts of city officials, environmental organizations, and the community at large will be instrumental in navigating the challenges ahead and upholding the legacy of Toledo’s commitment to environmental stewardship.