Understanding Turbidity: Why It Matters for Water Quality
Understanding Turbidity: Why It Matters for Water Quality
Introduction
Welcome to the world of water quality! If you’ve ever noticed a glass of water that looks like it just got back from a mud wrestling contest, you’ve encountered turbidity. But what exactly is turbidity, and why should it matter to anyone who isn’t a fish or a water treatment plant operator? Simply put, turbidity is a measure of the cloudiness or haziness in water caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye.
The clarity of water is not just about aesthetics; it’s crucial for environmental health, human safety, and industrial processes. Turbidity affects everything from the photosynthesis process in aquatic plants due to reduced light penetration to fish habitats that suffer when suspended particles cloud their living spaces. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), high turbidity levels can interfere with disinfection processes and lead to increased levels of disease-causing microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses.
“Turbidity is more than just an issue of water clarity; it’s an essential indicator of overall water quality,” says Dr. Jean Morrison, a renowned environmental scientist.
But let’s not get too cloudy on the technical details yet (pun intended). Picture this: you’re standing by your favorite river spot, where the sediment load in rivers might have jumped up because of recent stormwater runoff. That natural event alone can significantly impact turbidity, making those once-clear waters resemble chocolate milk!
- Sources of Turbidity: Includes runoff from agriculture, urban areas, and industrial waste discharge.
- Impact on Ecosystems: High sediment concentration can clog fish gills and smother aquatic plants.
- Turbidity Measurement: Typically measured in Nephelometric Turbidity Units (NTU) using specialized sensors.
Curious about what makes your river trips less scenic and more murky? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the depths (pun intended) of understanding turbidity—its causes, effects, and why maintaining optical clarity in our waterways is as crucial as never mixing milk with orange juice. Spoiler alert: Neither ends well!
What is Turbidity?
Ever peered into a glass of water and wondered why it’s not as clear as your grandmother’s crystal vase? That perplexing cloudiness you might see is what we term as “turbidity.” Simply put, turbidity is the measure of the degree to which water loses its transparency due to the presence of suspended particles. Imagine these particles as nature’s confetti celebrating in your drink—though not quite the celebration you’d want at your table!
These suspended particles can include a variety of substances such as clay, silt, finely divided organic and inorganic matter, plankton, algae, and even microscopic organisms. It’s like an aquatic party where everyone is invited but nobody knows how to leave. The higher the concentration of these materials, the murkier and less transparent the water appears.
The Science of Measuring Turbidity
Turbidity is typically measured in Nephelometric Turbidity Units (NTU), which might sound like something straight out of a sci-fi movie, but it’s actually a critical component for assessing water quality. To get technical for a moment, when light passes through water, it gets scattered by the suspended particles; an instrument called a turbidity sensor measures this scattering of light.
“Turbidimeters are used by scientists worldwide to provide accurate data on sediment concentration and help ensure compliance with drinking water standards.” — Source: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The NTU scale serves as an essential metric in environmental monitoring and helps us understand just how turbid or clear our waterways are. Water with an NTU rating below 1 is typically considered very clear; meanwhile, levels above 5 NTUs start raising eyebrows—and possibly health concerns.
Why Should We Care About Turbidity?
- Aquatic Ecosystem Health: High turbidity can significantly reduce light penetration in turbid waters, impacting photosynthesis for plants and algae.
- Fish Habitat: Excessive sediment load can degrade fish habitats and negatively affect their breathing through clogged gills.
- Water Treatment Costs: Increased levels can also raise costs related to water filtration systems necessary to achieve safe drinking water standards.
The causes of turbidity range from natural events like riverbed erosion to human-induced activities such as industrial waste discharge and stormwater runoff impact. Each plays its role in influencing sedimentation rates in lakes or rivers.
Navigating through these factors highlights why understanding and managing turbidity is crucial—not just for those monitoring our taps but also for promoting sustainable practices that safeguard our precious water resources.
The Importance of Water Clarity and Quality
Ever looked out over a pristine lake and thought, “Wow, I can see right to the bottom!”? That’s the magic of water clarity at work. But what exactly do we mean by water clarity, and why is it crucial for our water quality? Let’s dive in—pun intended!
Water clarity refers to how clear or transparent the water is. This might sound like a trivial detail, but it’s actually a big deal in the world of water quality. Clear waters are typically indicators of low levels of suspended particles, which means fewer sediments, plankton, and industrial waste floating around. This isn’t just good news for those with an inclination for snorkeling; it’s vital for maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems.
Why Does Clarity Matter?
- Aquatic Life: Fish and other aquatic organisms rely on clear waters for survival. High turbidity can block sunlight penetration, essential for photosynthesis in aquatic plants. This disruption can lead to reduced oxygen levels and impact fish habitats negatively.
- Human Consumption: Turbidity levels are closely monitored in drinking water standards because they can indicate contamination by pathogens or chemicals. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), drinking water should not exceed a turbidity level of 1 NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Units).[1]
- Ecosystem Health: When sediment concentration increases due to stormwater runoff or riverbed erosion, it clouds waters and harms delicate ecosystems. Algal blooms thrive in these conditions, further degrading water quality.
Maintaining water clarity is not just about keeping our lakes Instagram-worthy. It’s an essential part of monitoring environmental health and ensuring safe drinking supplies. Methods like coagulation and flocculation are often employed in treatment processes to enhance clarity by removing suspended solids before they become a nuisance—or worse.
“Water is life’s matter and matrix, mother and medium.” — Albert Szent-Györgyi
The next time you gaze into a crystal-clear body of water or turn on the tap at home, spare a thought for the unsung heroes working tirelessly behind the scenes: those measuring turbidity levels, implementing filtration systems, and ensuring that clarity equals quality.
For more insights on how clear versus turbid waters stack up or about sustainable practices ensuring future conservation efforts, check out our resources here at Water & Wastewater.
[1]U.S. Environmental Protection Agency – Turbidity Standards
Causes of Turbidity
Have you ever poured yourself a glass of water, only to be greeted by murkiness that resembles a swamp more than spring water? Welcome to the world of turbidity! But what exactly causes this cloudiness in water? Let’s dive into some of the main culprits that lead to turbid waters.
Natural Causes
- Sediment Load from Rivers and Streams: Moving water is like nature’s own silt shaker. Erosion from riverbanks can lead to suspended particles that reduce water clarity. According to the US Geological Survey, sedimentation rates in rivers can vary based on factors such as rainfall and land use.
- Algae Blooms: When algae decide to throw a party, they bring along their friends: cloudiness and reduced optical clarity. Algae growth can spike due to increased nutrients, often from agricultural runoff, affecting light penetration and sometimes resulting in fish habitat degradation.
- Plankton Density: These microscopic organisms contribute significantly to turbidity levels. Their presence is essential for aquatic ecosystems but can turn your crystal-clear lake into a cloudy mystery.
Human-Induced Causes
- Industrial Waste Discharge: Factories and plants sometimes discharge waste that includes suspended solids, contributing significantly to turbidity. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates these discharges under the Clean Water Act (EPA).
- Agricultural Runoff: Fertilizers and pesticides make their way into waterways during heavy rain, increasing sediment concentration. This runoff not only adds nutrients but also increases turbidity levels, impacting drinking water standards.
- Construction Activities: Construction work near waterways disturbs soil and increases erosion, leading directly into nearby rivers or lakes with a higher concentration of suspended particles.
“The increase in global population will continue to exacerbate the impact of these human activities on water bodies worldwide.” – UN World Water Development Report
If you’re interested in how these factors are addressed through treatment processes like coagulation and flocculation, be sure to explore our detailed article on essential techniques for maintaining water transparency through effective treatment methods: Coagulation and Flocculation: Essential Techniques for Water Treatment.
Turbid waters might seem like just an aesthetic issue at first glance, but understanding their causes is crucial for safeguarding aquatic ecosystem health and ensuring clean drinking water standards. Now that you’re versed in the causes of turbidity, you have one less reason to fear cloudy cups of H2O!
Turbid Water Effects on Aquatic Ecosystems
Imagine you’re trying to enjoy a leisurely swim, but then someone dumps a truckload of mud into the pool. Not exactly the serene experience you were hoping for, right? That’s pretty much what turbid water does to aquatic ecosystems. Turbidity, the cloudiness or haziness in water caused by large numbers of individual particles, can have profound and often disruptive effects on aquatic life.
The Light Dilemma
One of the primary issues with turbid water is its impact on light penetration. The suspended particles block sunlight from reaching underwater plants and algae, which rely on photosynthesis to produce energy. Without adequate sunlight, these photosynthetic organisms struggle to survive, creating a ripple effect through the food chain. This is especially concerning in regions where species like seagrasses form essential habitats for marine life.
Fish Habitat Degradation
Turbidity not only affects plant life but also fish habitats. High levels of suspended solids can smother fish eggs and reduce oxygen levels in the water, leading to stunted growth or even death. Fish that rely on sight for feeding or avoiding predators find themselves at a disadvantage in cloudy waters. Moreover, sedimentation rates in lakes can increase due to turbidity, further disrupting aquatic life.
Turbidity’s Unwanted Guests: Algae Blooms
High turbidity levels are often associated with nutrient runoffs—thanks to stormwater or industrial discharges—which can lead to algal blooms. These blooms not only look unsightly but they also consume massive amounts of oxygen when they decompose. This process can result in hypoxic conditions or “dead zones,” where little marine life can survive.
“Increased sediment loads from riverbed erosion due to human activities have shown significant increases in turbidity levels across various waterways worldwide.” – Environmental Monitoring Reports
The Big Picture
- Loss of Biodiversity: Reduced light and lower oxygen levels mean fewer species thrive.
- Food Chain Disruption: A decrease in plant-based organisms leads to less food for herbivores and subsequently carnivores.
- Ecosystem Health: Prolonged high turbidity can lead to long-term ecological impairments that take decades to reverse.
While turbid waters present challenges, understanding and mitigating these impacts through effective treatment processes can help preserve our precious aquatic environments. Remember, clearer water means healthier ecosystems—and maybe even more enjoyable swims!
Measuring Turbidity Levels: Tools and Techniques
When it comes to understanding turbidity, think of yourself as a detective on a mission. Your goal? To uncover the mysteries of water cloudiness with the right tools and techniques. Whether you’re an environmental scientist, a water treatment professional, or just someone who wants their backyard pond to look less like pea soup, measuring turbidity is essential.
The NTU Scale and Its Significance
The cornerstone of turbidity measurement is the NTU scale (Nephelometric Turbidity Units). Think of it as the GPA for water clarity—except here, higher numbers aren’t exactly commendable. Typically, drinking water is required to register below 1 NTU to meet most drinking water standards. A higher NTU can indicate anything from sediment concentration to algae growth.
Turbidity Sensors: The Sherlock Holmes of Water Quality
Enter turbidity sensors, your trusty magnifying glass in this aquatic investigation. These high-tech devices come equipped with light detectors that measure the scattering effect of suspended particles in water. For instance:
- Nephelometers: These measure scattered light at a 90-degree angle and are widely used for their precision.
- Turbidimeters: Similar to nephelometers but often more compact, making them perfect for fieldwork.
- Portable Turbidity Meters: Handy tools that provide quick readings on-site to detect changes due to stormwater runoff or industrial discharge.
The Art (and Science) of Optical Clarity
Turbidity isn’t just about cloudy versus clear waters; it’s about understanding the science behind these changes. By using these instruments, we can assess how sediment load in rivers impacts aquatic ecosystem health or how light penetration in turbid waters affects photosynthesis. After all, without sunlight reaching underwater plants, you’d probably have some very grumpy seaweed on your hands!
“Turbidity is nature’s way of telling us what it was up to last night—whether that’s a heavy rainfall or an influx of suspended solids from construction sites.” – Anonymous Water Enthusiast
If you’re looking into more advanced methods for tackling turbidity issues, consider exploring our guide on coagulation and flocculation techniques, which are essential for optimizing water clarity.
Certainly, understanding turbidity levels and employing the right measurement tools can make you not only a guardian of your local waterways but also potentially save you from drinking something best left to mythical swamp creatures!
The Role of Turbidity in Water Treatment Processes
When it comes to water treatment processes, turbidity isn’t just a fancy word that engineers use at dinner parties. It’s a critical parameter that can make or break the clarity and safety of our drinking water. So, why does turbidity matter so much in water treatment? Let’s dive into it—without making a splash!
Understanding Turbidity’s Impact
Turbidity refers to the cloudiness or haziness in water caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. Think of it as the “fog” of the aquatic world. These suspended particles can include silt, clay, organic matter, algae, and other microscopic organisms. The higher the turbidity level, measured in Nephelometric Turbidity Units (NTU), the murkier the water appears.
- Sediment concentration: Increased sediment concentration can affect not just the aesthetic but also the safety of drinking water.
- Suspended solids: These are bits and pieces that need to be removed for effective water filtration systems.
Turbidity’s Role in Treatment Stages
Turbid waters require more rigorous treatment methods. Here’s how turbidity fits into various stages of water treatment:
- Coagulation and Flocculation: Here, chemicals are added to form tiny sticky particles called “flocs” which attract dirt particles. A clump party ensues!
- Settling and Sedimentation: Once clumped together, these flocs settle at the bottom due to gravity.
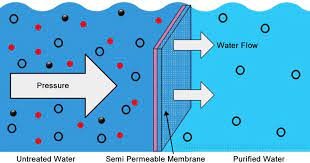
- Filtration: The clearer water on top then goes through filters made up of sand, gravel, and sometimes charcoal which remove any smaller particles that remain.
This three-step process is crucial for reducing turbidity levels because high turbidity can interfere with disinfection processes like chlorination by harboring pathogens inside suspended solids. Imagine trying to wash dishes with muddy hands—it’s quite ineffective!
The Bigger Picture: Environmental Monitoring
Apart from being a pivotal factor in treating drinking water, monitoring turbidity is essential for assessing environmental health. For instance:
- Aquatic Ecosystem Health: High turbidity can block light penetration necessary for photosynthesis in aquatic plants.
- Fish Habitat Degradation: Excessive suspended particles can clog fish gills and smother eggs.
“Turbid waters can create unsuitable habitats for many aquatic organisms.” – Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
If you’re thirsty for more information about how clouds impact your water quality or want tips on sustainable practices in water management, remember there’s always more bubbling up at Water & Wastewater: Your Source for Water Clarity.
Conclusion: The Need for Monitoring Turbidity
So, why all the fuss about turbidity and why should it matter to you? Well, imagine trying to find your favorite pair of socks in a room filled with fog—that’s essentially what aquatic life deals with in turbid water! Monitoring turbidity isn’t just a fancy science project; it’s vital for maintaining water quality, supporting aquatic ecosystems, and ensuring human health. Let’s dive into the reasons why keeping an eye on those murky waters is so essential:
- Environmental Health: High turbidity can stunt plant photosynthesis by limiting light penetration. This affects not only plant life but also fish and other aquatic organisms that rely on these plants for food and habitat.
- Human Health: Turbidity serves as a proxy for detecting potential pathogens in drinking water. A rise in turbidity levels could signal a presence of contaminants that may lead to waterborne diseases.
- Compliance with Standards: Regulatory bodies like the EPA have set specific standards for drinking water, often using the NTU scale (Nephelometric Turbidity Units) as a benchmark. Not meeting these standards can lead to hefty penalties and public health risks.
- Ecosystem Balance: Too much sediment concentration due to reasons like riverbed erosion or industrial waste discharge disrupts the ecological balance, affecting biodiversity adversely.
Turbidity measurement is thus more than just about achieving optical clarity; it’s about sustaining life itself—both aquatic and human. Using advanced technologies like turbidity sensors and real-time monitoring systems can significantly help in assessing and controlling sediment loads in rivers or lakes.
“Monitoring turbidity effectively ensures that we are not only meeting necessary regulations but are also helping preserve our natural resources for generations to come,” says an industry expert.
For those intrigued by the mechanics of how we tackle these issues, check out our comprehensive guide on Coagulation and Flocculation: Essential Techniques for Water Treatment. It’s about time we give our waters the clarity they deserve—after all, Mother Nature wouldn’t want her streams running fashionably cloudy!
“`