Vacuum Disc Filter
Understanding Vacuum Disc Filters: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Industrial filtration technologies are crucial for various sectors, from mining to chemical processing. Among these, the vacuum disc filter stands out for its efficacy in solid-liquid separation. Known for their versatility and efficiency, vacuum disc filters have become a staple in many industrial processes. This article delves into the intricacies of vacuum disc filters, examining their design, operation, applications, advantages, limitations, and future prospects.
1. Historical Background
The vacuum disc filter was invented in the early 20th century to address the need for effective slurry dewatering in mining industries. Initially, these filters served primarily in the pulp and paper industry, but they quickly found applications across various sectors due to their efficiency and adaptability. Over the years, technological advancements have improved the materials and technologies used in these filters, making them more effective and durable.
2. Design and Construction
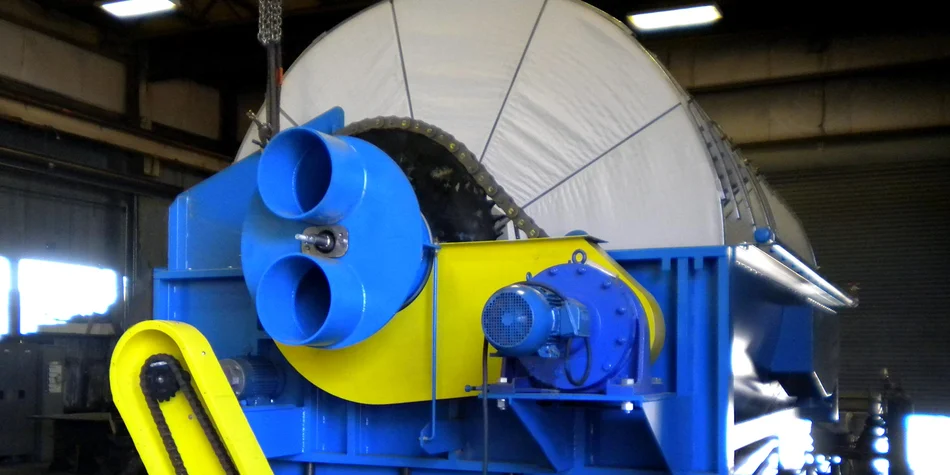
Vacuum disc filters are made up of several key components that facilitate their main function: separating solids from liquids in slurry.
a. Structure
-
- Rotary Disc: The heart of the vacuum disc filter is its rotating disc. Typically comprising several discs mounted on a central shaft, these discs are divided into sectors. Each sector is covered with a filter cloth and submerged in a slurry tank during operation.
- Rotary Disc: The heart of the vacuum disc filter is its rotating disc. Typically comprising several discs mounted on a central shaft, these discs are divided into sectors. Each sector is covered with a filter cloth and submerged in a slurry tank during operation.
-
- Filter Cloth: The choice of filter cloth is pivotal as it determines the particle size that can be captured. Modern vacuum disc filters use synthetic fabrics to enhance durability and chemical resistance.
- Filter Cloth: The choice of filter cloth is pivotal as it determines the particle size that can be captured. Modern vacuum disc filters use synthetic fabrics to enhance durability and chemical resistance.
-
- Piping System: A network of pipes and tubes transports slurry to the filter and withdraws the filtered liquid, ensuring continuous operation.
- Piping System: A network of pipes and tubes transports slurry to the filter and withdraws the filtered liquid, ensuring continuous operation.
-
- Vacuum System: This includes vacuum pumps and receivers, which create the pressure difference necessary for filtration.
b. Materials
Vacuum disc filters are usually constructed from materials like stainless steel or reinforced plastics, chosen for their strength and resistance to corrosive materials. Continuous advancements in material science have brought forth components capable of withstanding extreme conditions while maintaining efficiency.
3. Operating Principles
The operation of a vacuum disc filter involves continuous rotation, vacuum application, and, subsequently, cake formation and removal.
a. Filtration Process
-
- Slurry Inlet: The slurry is introduced into a tank where the lower part of the rotating discs is submerged.
- Slurry Inlet: The slurry is introduced into a tank where the lower part of the rotating discs is submerged.
-
- Vacuum Application: As the disc rotates, a vacuum is applied to the underside of the filter sectors. This vacuum draws liquid through the filter cloth while leaving solids on the surface as a filter cake.
- Vacuum Application: As the disc rotates, a vacuum is applied to the underside of the filter sectors. This vacuum draws liquid through the filter cloth while leaving solids on the surface as a filter cake.
-
- Cake Drying: Continued vacuum application removes additional moisture from the filter cake as the disc rotates out of the slurry bath.
- Cake Drying: Continued vacuum application removes additional moisture from the filter cake as the disc rotates out of the slurry bath.
-
- Cake Discharge: Once the cake reaches a particular section, it is mechanically scraped off or blown off using compressed air, depending on the design.
b. Continuous Operation
One of the key features of vacuum disc filters is their ability to operate continuously, which increases throughput and efficiency compared to batch systems.
4. Applications
Vacuum disc filters are utilized in a wide range of industries due to their versatility.
a. Mining
In mining, vacuum disc filters are critical for dewatering mineral slurries, predominantly iron ore and phosphate.
b. Chemical Processing
These filters help manage waste streams and recover valuable products in chemical production processes.
c. Food and Beverage
In the food sector, vacuum disc filters are used in applications ranging from sugar processing to edible oil purification.
d. Wastewater Treatment
Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment facilities use these filters to remove suspended solids before water discharge or reuse.
5. Advantages
a. Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
The continuous operation of vacuum disc filters allows for high throughput, making them cost-effective in large-scale operations.
b. Versatility
Their ability to filter a wide range of particle sizes makes vacuum disc filters suitable for diverse applications across sectors.
c. Scalability
Vacuum disc filters can be scaled easily to meet different demands. By adjusting the number of discs or the vacuum pressure, operators can optimize the system for specific processes.
d. Durability
Advancements in materials and design have made modern vacuum disc filters highly durable, needing less frequent maintenance and repair.
6. Limitations
Despite their advantages, vacuum disc filters have some limitations that should be considered when selecting a filtration technology.
a. Initial Capital Cost
The initial investment in a vacuum disc filter system can be significant, although the long-term benefits typically outweigh this cost.
b. Maintenance Requirements
While durable, vacuum disc filters do require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, including periodic replacement of filter cloths and maintenance of the vacuum system.
c. Specific Filtration Limits
Certain slurries with very fine particulates or highly viscous compositions may pose challenges and require specific configurations to filter effectively.
7. Innovations and Future Prospects
a. Technological Advancements
Continuous innovation in filter materials and mechanics promises to overcome current limitations and introduce more efficient, resilient systems. Developments in automation and digital monitoring allow operators to optimize performance and reduce humans’ intervention.
b. Environmental Considerations
With increased attention on sustainability and resource efficiency, vacuum disc filters are being adapted to reduce energy consumption and enhance recovery rates of valuable materials from waste streams. Advances in eco-friendly materials and processes are complementing these efforts.
c. Market Trends
The demand for vacuum disc filters is expected to grow with rising industries in emerging markets. With the world’s shift towards sustainability, industries will push for more efficient solid-liquid separation technologies, further driving innovation and adoption.
Conclusion
Vacuum disc filters represent a critical technology for effective industrial filtration. Understanding their mechanics, benefits, and limitations can significantly impact operational efficiency and productivity across industries. As advancements continue to emerge, vacuum disc filters will likely play an even more integral role in the global push towards industrial sustainability and innovation. Whether in mining, food processing, or chemical production, vacuum disc filters are poised to remain a key player in enhancing industrial processes.


